The aim of this study was to describe t.
Ct scan orbital floor mesh.
Psi placement over failed pre bend mesh.
The matrixmidface preformed orbital plates are designed from ct scan data.
Orbital floor designed from ct scan data the three dimensional implants closely approximate the topographical anatomy of the hu man orbital floor and medial wall to provide accurate recon struction even after significant two wall fractures 5 6 preformed three dimensional shape.
For minimal bending and cutting which reduces the amount of time.
The overlying colored line in the medial wall and orbital floor area indicate the preoperative virtual planning that is superimposed on the mesh reconstructed area.
In case the orbital floor is not properly reconstructed correction of shape and position of the implant is recommended followed by a.
This x ray shows the classic transition zone.
Coronal slice of a postoperative ct scan taken after transconjunctival repair of the complete left medial orbital wall and orbital floor.
A ct scan with axial and coronal views is optimal.
For most orbital fractures the imaging study of choice is ct scan.
Surgical treatment was performed using subciliary inferior palpebral approach to explore the orbital floor and placement of the titanium mesh and an intraoral antrostomy for endoscopy to magnification of the surgical field and adaptation of the mesh.
To design implants for orbital reconstruction rapid prototype models can be derived from digital imaging and communications in medicine dicom data obtained from the patient s computed tomography ct scan.
Postoperative ct scan analysis shows that all treatments restored orbital volume and.
Intraoperative computed tomography ct scan may facilitate this procedure.
These plates consist of implants that closely approximate the topographical anatomy of the human orbital floor and medial wall and are intended for use in a selective craniomaxillofacial trauma.
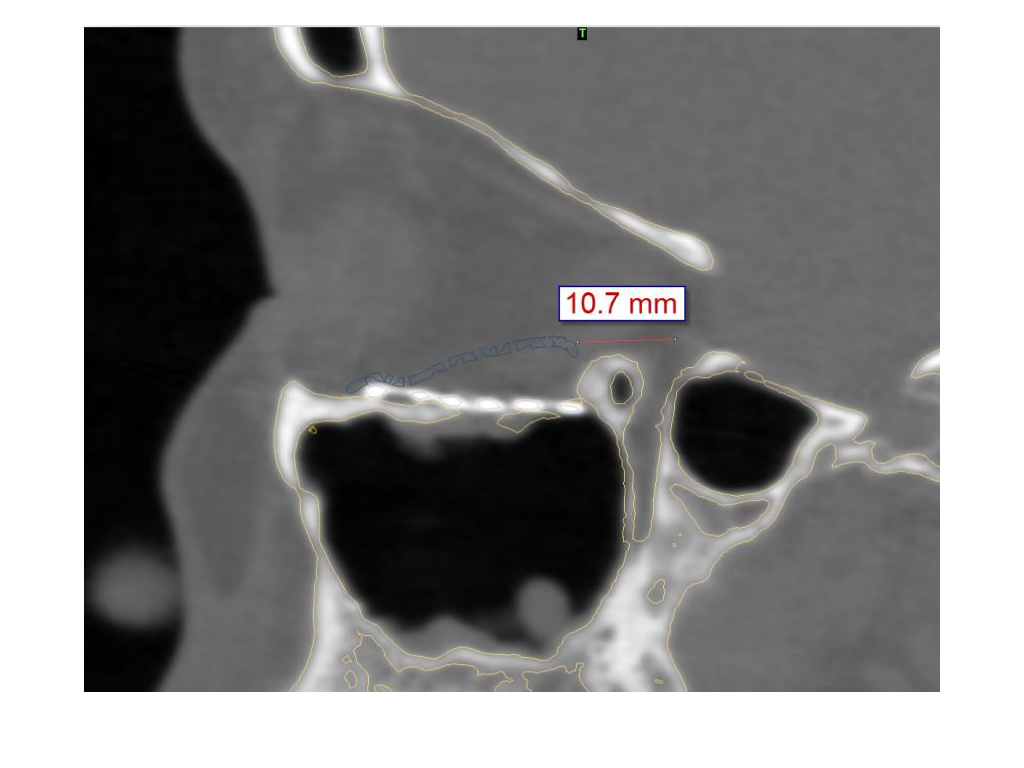
The correct anatomic shape of the titanium mesh used for orbital floor reconstruction can be verified in the intraoperative ct scan.
This confirms that there is no need for further corrections in this case.
Ask for thin cuts 2 3 mm with specific attention to the orbital floor and optic canal.
6 7 see the image below.
This study was prospectively conducted on 10 patients with unilateral orbital floor fractures caused by accident or falls.
The sagittal plane computed tomographic ct scan has been proposed as the most important radiologic view in the diagnosis of orbital floor fractures.
In intervention group n 5 the ct scan slices were used for generating 3d reconstruction of both affected and unaffected orbits.